Originally published at: https://nextcloud.com/blog/all-you-need-to-know-about-facial-recognition-technology-and-the-nextcloud-recognize-app/
Face recognition often gets a bad rap, as it’s associated with privacy infringements. However, Nextcloud software engineer Marcel Klehr would argue that the issue isn’t the technology itself, but how it’s used. To understand his thoughts, let’s first dive into how computers recognize faces.
How do computers recognize faces?
Face recognition is a system and technology that matches a human face from a digital image or a video frame against a database of faces.
The idea came about over 60 years ago when researchers tried computing the distances between an individual’s nose, eyes and mouth to determine their identity, but has since been fine tuned to be quite accurate and useful today.
Just like how the brain has neurons which process actions, so do artificial neural networks on a computer. Computerized neurons process and compute data recognizing statistical patterns. An (over) simplified example would go like this: you have a ‘network’ with 5 ‘input’ neurons (where you feed in information) and 1 ‘output neuron’ which shows you the outcome. The network does only one thing: tell you if something is a banana or not!
Each ‘neuron’ has to be told a type of information. Say, you tell neuron 1 the color of the object you have, the second neuron the size, the third its shape, the fourth its smell and so on. Each neuron will, when given information on an object, tell the ‘output neuron’ on a scale of 1-10 if it thinks what it got is banana (like). For example, the color neuron would give a 10 on yellow, 8 on green and brown, 7 on black, but 0 on red. The ‘output neuron’ adds up all chances and at a threshold (it has to learn by itself, one of the great tricks of neurons) say ‘yes, this is a banana’. A neural network that recognizes faces functions a bit similar – yet vastly more complicated.
So you can train neurons to recognize something, but in order to do that you need a large set of data and a large amount of computer resources. That is why it’s taken so long for this type of deep learning to be accurate.
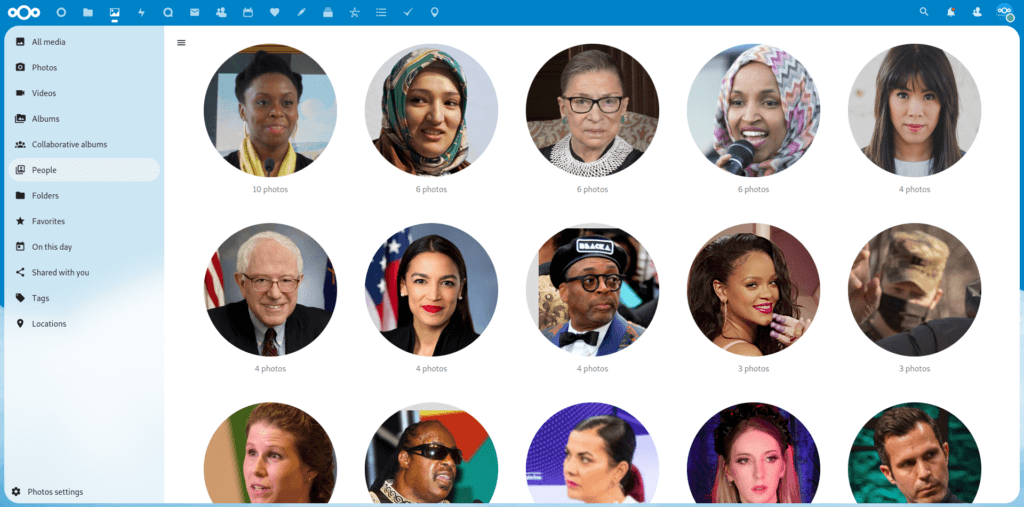
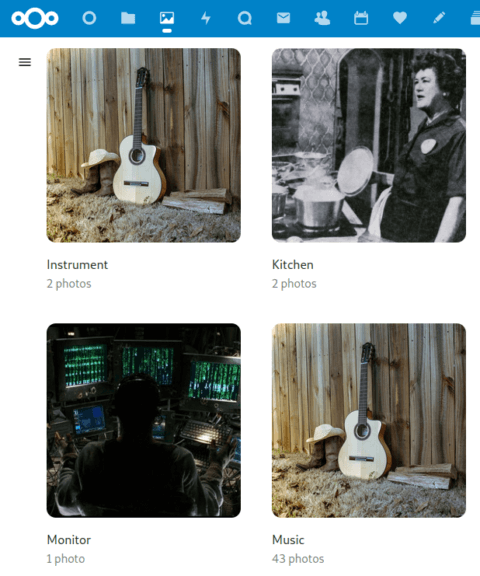
Once the system has been trained, you can then use face recognition to find and tag your family members, friends and more. You can even do object recognition to identify animals, nature and landmarks.
Recognize: A Nextcloud app
Google created and trained several neural network models that are free to use under an Apache license used by many open source projects like Recognize, the Nextcloud app created by Marcel.
To see which models are being used as well as a detailed explanation about how the app works, check out Marcel’s post here.
Recognize goes through your media collection and adds fitting tags which automatically categorizes your photos and music. It can recognize:
📷 👪 Faces from contact photos
📷 🏔 Animals, landscapes, food, vehicles, buildings and other objects
📷 🗼 Famous landmarks and monuments
👂 🎵 Music genres
The downsides and risks
Based on the way the face recognition model works, the model itself is not harmful towards privacy. Face recognition in Reconize happens on your local Nextcloud and your photos aren’t sent anywhere else.
But there are challenges. First, as explained – the models are trained on data. There are issues with where this data comes from and how it is put together. If one were to train a network on images from Instagram, and ask what the life of a human looks like, it’s not hard to imagine that the result would be hopelessly optimistic! Models thus bring the biases in their data with them. A computer is of course not racist or sexist, but models designed to help with hiring people have been show to exemplify these biases because the data used to train them contained these.
Beyond biases, one can ask if it is ok to take data stored for one reason and use it for training AI’s.
Stanford University researchers for example collected and used 10,000 photos from Flickr, which was legal under the Creative Commons license, to share with China’s National University of Defense Technology and an AI company that provided China with surveillance technology. That was likely not what the people who uploaded their photos had in mind.
All in all, when companies compile these large data sets, it’s not known what they will do with the data or if it will be exposed to vulnerabilities. It is important to trust the service you offer your data to and understand their policies on data privacy. And it is important to be aware of the limitations of AI and what it is being used for.