Split-brain DNS, also known as split-horizon DNS or split-view DNS, is a technique used in computer networking to manage how computers resolve domain names (like cloud.mydomain.tld) differently depending on whether they are inside or outside a specific network, typically an internal network. The main goal is to allow local connection from internal network and avoid looping connections from internal network through the public internet which adds delays and possibly reduce bandwidth.
This technique is much more powerful and convenient variant of frequent try to access the server locally using it’s LAN IP (local_network) which results in caveats like invalid share links while accessing the system internally and missing https causing browser TLS warnings.
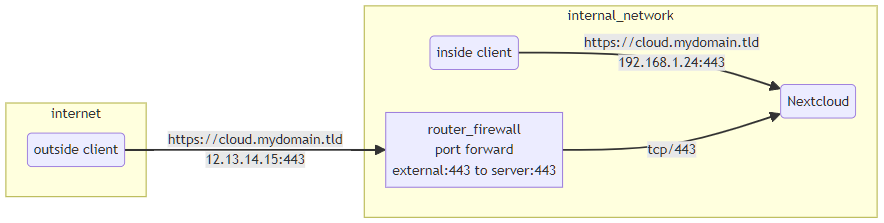
as you see in the image
- client from the internet resolve your public DNS name to a public IP address of your router/firewall which in turn sends all requests to an internal system using port forwarding
- clients from internal network resolve the public DNS name to an internal IP address of the application avoiding the loop through the public DNS server, public IP and possible up-/download limits of the external connection
how it works:
- Two sets of DNS records: splitbraindns provides two different sets of DNS records is for internal users on the internal network, and the other is for external users on the internet.
- Implementation: Split-brain DNS can be implemented in a couple of ways:
- Multiple DNS servers: Traditionally, separate external and internal DNS servers were used for internal and external requests.
- DNS policies: Modern DNS servers allow for creating policies that define how to answer requests based on the source address.
There are different methods to implement Split-brain DNS. Most common in self-hosting is a local DNS server which could be integrated into your router or external like popular Pi-Hole pihole or AdguardHome appliances (both offer additional DNS features e.g. advertisement blocking)
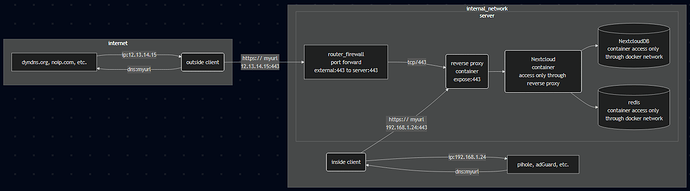
more complex view, showing internal and external DNS server:
flowchart LR
subgraph internet
dnsext[dyndns.org, noip.com, etc.]
clientext(outside client)
end
router_firewall[router_firewall<br>port forward<br>external:443 to server:443]
subgraph internal_network
clientint(inside client)
clientint-- https:// myurl<br>192.168.1.24:443 -->RP;
dnsint[pihole, adGuard, etc.]
subgraph server
RP(reverse proxy<br>container<br>expose:443)
Nextcloud(Nextcloud<br>container<br>access only through reverse proxy)
NextcloudDB[(NextcloudDB<br>container access only through docker network)]
redis[(redis<br>container access only through docker network)]
Nextcloud-->NextcloudDB
Nextcloud-->redis
router_firewall-- tcp/443 -->RP;
RP-->Nextcloud
end
end
dnsint-- dns:myurl --->clientint;
clientint-- ip:192.168.1.24 --->dnsint;
clientext-- https:// myurl<br>12.13.14.15:443 -->router_firewall;
dnsext-- ip:12.13.14.15 ---->clientext;
clientext-- dns:myurl ---->dnsext;